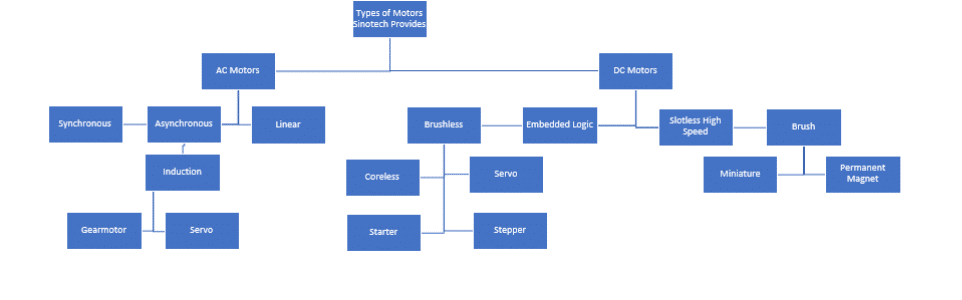
AC motors have been the workhorses of numerous industries for over a century and are still widely used today. As one of the earliest electric motors developed for industrial use, AC motors enabled factories and businesses to power different types of equipment. Though newer motor technologies have come along since then, AC motors remain an attractive choice for applications that demand high reliability, flexibility of speed control, and ease of maintenance over long operational periods.
Whether used to drive conveyor belts in a packaging facility or power ventilation systems in building HVAC equipment, AC motors fulfill a variety of rotational motion needs through their combination of robust mechanical design and proven control methods that maximize efficiency. Let us explore some of the critical uses of AC motors across diverse industries and the differences between AC vs. DC motors.
What Are The Common Uses for AC Motors?
AC motors have substantial and diverse applications due to their versatility. AC motors have powered various applications in many industries, from simple appliances to more powerful machinery in demanding facilities. That said, here are some of the common uses for AC motors:
- Appliances: The uses of AC motors are vast, so they can be found in numerous home appliances, such as washing machines, drills, ovens, refrigerators, and water heaters.
- Food and beverage: The food and beverage processing industry relies on AC motors because they can power essential machinery, such as conveyor belts, mixers/blenders, and packaging machines. In addition, their quiet operation is ideal in applications where noise is a factor.
- HVAC: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems in buildings require AC motors for powering fans, compressors, and pumps.
- Automotive: Modern electric vehicles are equipped with high-performance AC motors to power the wheels and control speed.
- Manufacturing: AC motors are found in assembly lines and robotics systems. Their functions are essential in numerous manufacturing processes.
- Agriculture: Farming equipment like tractors and irrigation systems utilize AC motors due to their longevity and optimal performance.
With nearly endless applications, the functions of AC motors deliver irrefutable benefits that can efficiently convert and provide power to numerous systems, preventing downtimes in a broad range of operations and production processes.
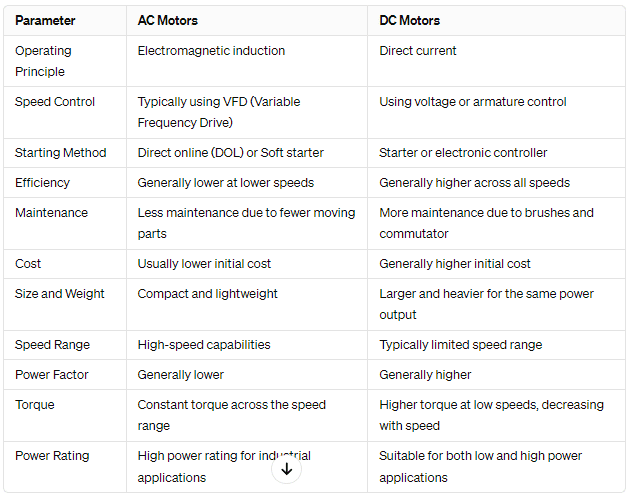
AC vs. DC Motors
AC motors are not inherently less efficient than DC motors. Each motor type carries its pros and cons, with efficiency influenced by factors like application, design, and operating conditions.
Historically, DC motors have commonly been viewed as more efficient than AC motors for specific applications because of variations in their design and control mechanisms. Some factors contributing to the perception of DC motors as more efficient in certain situations include:
- Control mechanisms: DC motors have long been known for their superior speed and torque control, particularly at low speeds, in contrast to early AC motor models. This high level of precision enables improved efficiency in applications that demand accurate speed regulation.
- Starting torque: DC motors generally demonstrate greater starting torque than AC motors, particularly in series-wound or compound-wound DC motors. This increased starting torque proves beneficial in applications that involve frequent start-stop cycles or when dealing with heavy loads.
- Brushless design: Conventional AC motors, like induction motors, depend on brushes and commutators for functioning, causing energy wastage and maintenance challenges. In contrast, numerous DC motors, especially brushless DC motors, eliminate the requirement for brushes and commutators, cutting down on friction and enhancing efficiency.
- Power factor: In specific scenarios, AC motors may exhibit lower power factors in contrast to DC motors, leading to extra losses in the electrical system. Nevertheless, advancements in modern AC motor designs and power electronics have notably enhanced power factor correction and efficiency.
- Specific applications: AC motors find extensive use in many industries, yet DC motors could be favored for certain applications due to their unique traits that provide a performance edge. This is particularly evident in specific traction applications or environments that require precise speed control.
Advancements in technology, like the enhanced variable frequency drives (VFDs) for AC motors and motor design improvements, have reduced the efficiency gap between AC and DC motors in various applications. Both motor types can now achieve high-efficiency levels based on specific needs and operating conditions.
Understanding AC Motors and Its Uses Before Making a Purchase
AC motors come in many shapes and sizes, so they are readily available for a wide range of needs. Looking for a reputable AC motor manufacturer like Sinotech with a long list of product selections means finding different options to fit your needs.
From small single-phase motors to larger three-phase motors for more powerful machinery, understanding AC motors and their uses will help you decide when to select the appropriate product for your project.
If you want to know more about our variety of AC motors, do not hesitate to contact us today. You may also check out our consultancy services, and we can find a suitable solution based on your company’s exacting requirements!